Thermal pollution example
Move over each number to learn more.

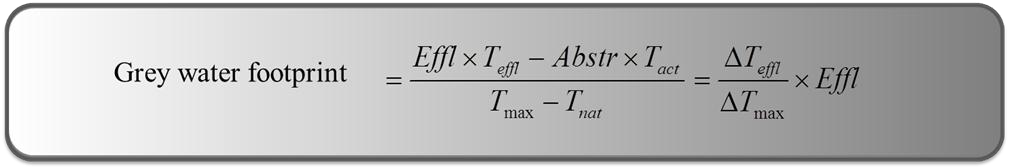 1
The load is now equal to the difference between the abstracted heat and the added heat in the form of a warm effluent.
2
When the effluent volume is equal to the abstraction volume, the equation gets a bit simplified.
The grey water footprint is then equal to the increased temperature in the effluent divided by the
maximum increase in the temperature of the receiving water body times the effluent volume.
1
The load is now equal to the difference between the abstracted heat and the added heat in the form of a warm effluent.
2
When the effluent volume is equal to the abstraction volume, the equation gets a bit simplified.
The grey water footprint is then equal to the increased temperature in the effluent divided by the
maximum increase in the temperature of the receiving water body times the effluent volume.