Point-source pollution example
Move over each number to learn more.

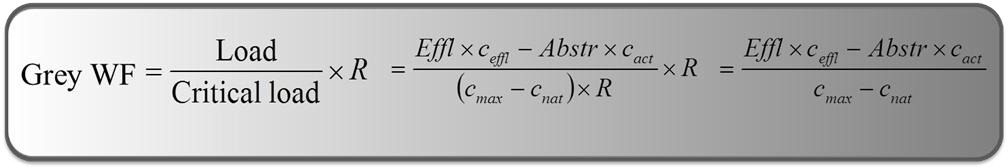 1
The grey water footprint is calculated by dividing the pollutant load by the
critical load in the receiving water body and multiplying that by the runoff of
the water body. The runoff, R, is expressed in terms of volume per unit of time,
for example cubic metre per day. The load and the critical load are both expressed
in mass per unit of time, for example kilogram per day.
2
The critical load is equal to the difference between the maximum acceptable
concentration for that chemical and the natural concentration of the chemical in the
receiving water body, multiplied by the runoff. In case of a point-source pollution,
the load can be calculated as the effluent volume multiplied by the concentration of the
chemical effluent, minus the water abstraction volume multiplied by the actual concentration
in the abstracted water. Abstraction, effluent and runoff are all measured in terms of water volume
per unit of time.
3
The runoff, R, cancels from the equation, leaving four different concentrations:
1
The grey water footprint is calculated by dividing the pollutant load by the
critical load in the receiving water body and multiplying that by the runoff of
the water body. The runoff, R, is expressed in terms of volume per unit of time,
for example cubic metre per day. The load and the critical load are both expressed
in mass per unit of time, for example kilogram per day.
2
The critical load is equal to the difference between the maximum acceptable
concentration for that chemical and the natural concentration of the chemical in the
receiving water body, multiplied by the runoff. In case of a point-source pollution,
the load can be calculated as the effluent volume multiplied by the concentration of the
chemical effluent, minus the water abstraction volume multiplied by the actual concentration
in the abstracted water. Abstraction, effluent and runoff are all measured in terms of water volume
per unit of time.
3
The runoff, R, cancels from the equation, leaving four different concentrations:-
Natural concentration (cnat)
concentration of the chemical in the water that would occur without human disturbances -
Actual concentration (cact)
can be higher than the natural one if ther is already pollution from upstream -
Effluent concentration (ceffl)
often higher than the concentration from the abstracted water -
Maximum acceptable concentration (cmax)
depends on the established water quality standards for the chemical considered;